Off-Grid vs Grid-Tied Inverters: What You Need to Know
 Dec 25,2023
Dec 25,2023
 Basen
Basen
Navigating the World of Inverters for Solar Energy Systems
In the realm of solar power systems, understanding the difference between off-grid and grid-tied inverters is crucial. This blog delves into the functionalities, benefits, and considerations of both types of inverters, helping you make an informed decision for your solar energy needs.
What is an Inverter?
Before diving into the specifics, it's important to understand what an inverter does. In solar power systems, an inverter converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is used in homes and businesses.
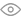
Off-Grid Inverters: Independent Power Generation
Off-grid inverters are designed for systems not connected to the utility grid. These are typically used in remote locations:
- Functionality: Off-grid inverters convert solar-generated DC into AC for immediate use. They often work in conjunction with battery storage systems to provide power when solar production is low.
- Benefits: Provides energy independence, ideal for remote or rural areas without grid access.
- Considerations: Requires a well-planned system to manage energy storage and usage efficiently.
Grid-Tied Inverters: Connected and Efficient
Grid-tied inverters are used in solar systems that are connected to the utility grid:
- Functionality: These inverters not only convert DC to AC but also synchronize the energy with the grid's frequency and voltage. Excess energy can be fed back to the grid, often earning credits through net metering.
- Benefits: Reduces electricity bills, offers reliability through the grid, and allows for financial incentives.
- Considerations: Relies on the grid; during power outages, most grid-tied systems will not provide backup power unless they have a battery system with a hybrid inverter.
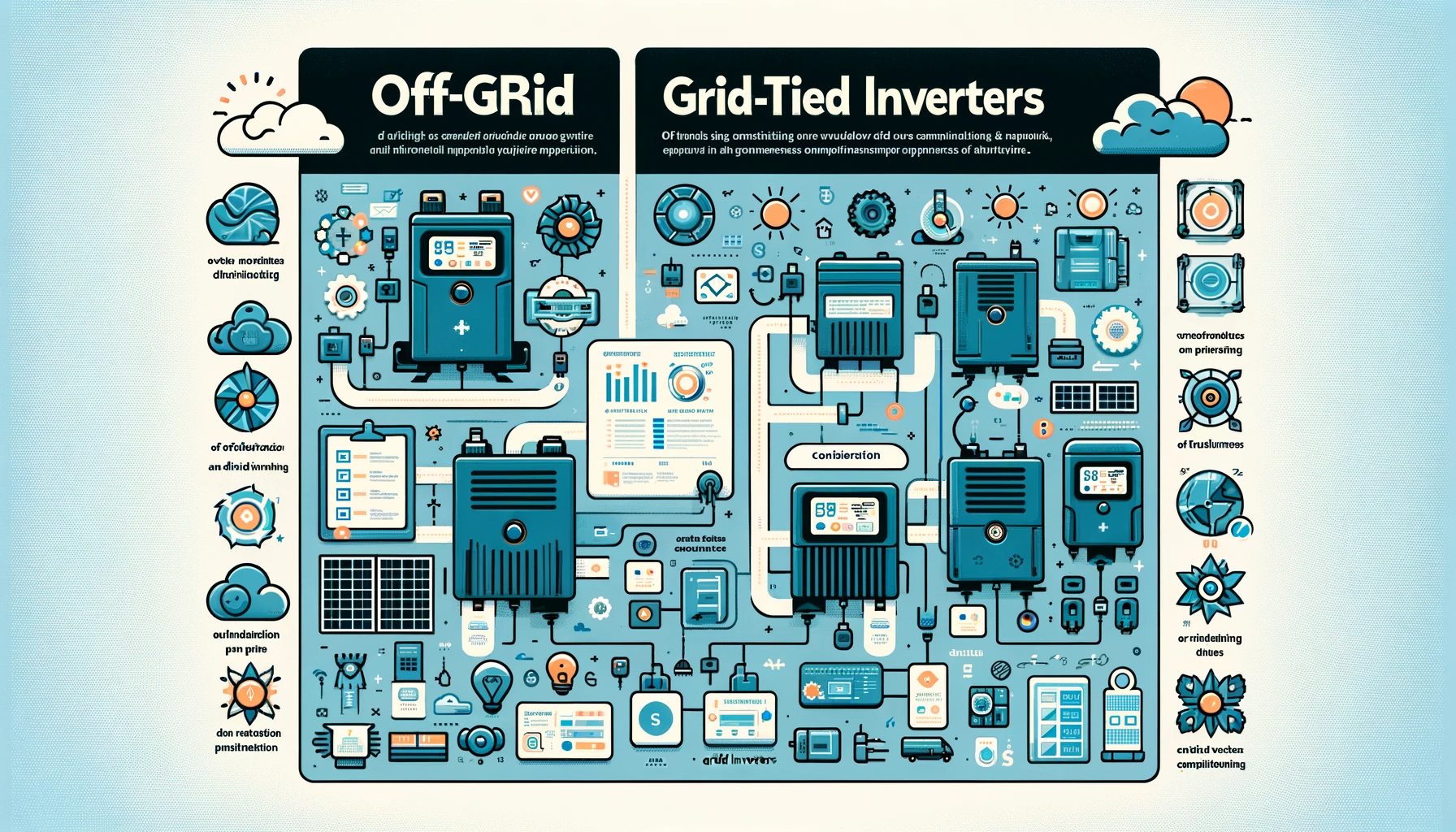
Hybrid Inverters: The Best of Both Worlds
Hybrid inverters combine the functionalities of both off-grid and grid-tied systems:
- Functionality: They can store excess energy in batteries and also feed into the grid. During outages, they can switch to off-grid mode, providing uninterrupted power supply.
- Benefits: Versatility, energy independence, and grid reliance when needed.
- Considerations: Higher initial investment, but offers more flexibility and energy security.
Making the Right Choice
Choosing between off-grid and grid-tied inverters depends on your specific needs:
- Location: If you are in a remote area, an off-grid system might be your only option.
- Energy Goals: If reducing your carbon footprint and energy bills is your goal, a grid-tied system is ideal.
- Backup Needs: For those requiring backup during outages, a hybrid system is the best solution.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Solar Journey
Whether you opt for an off-grid, grid-tied, or hybrid inverter, each serves a unique purpose in harnessing solar energy. Understanding your energy needs and goals is key to selecting the right inverter, paving the way for a more sustainable and efficient energy solution. With the right inverter, solar power becomes not just a source of energy, but a step towards a greener future.






 HOME
HOME Energy Storage Core - Insights into BMS Architecture
Energy Storage Core - Insights into BMS Architecture  You May Also Like
You May Also Like

 Tel
Tel
 Email
Email
 Address
Address